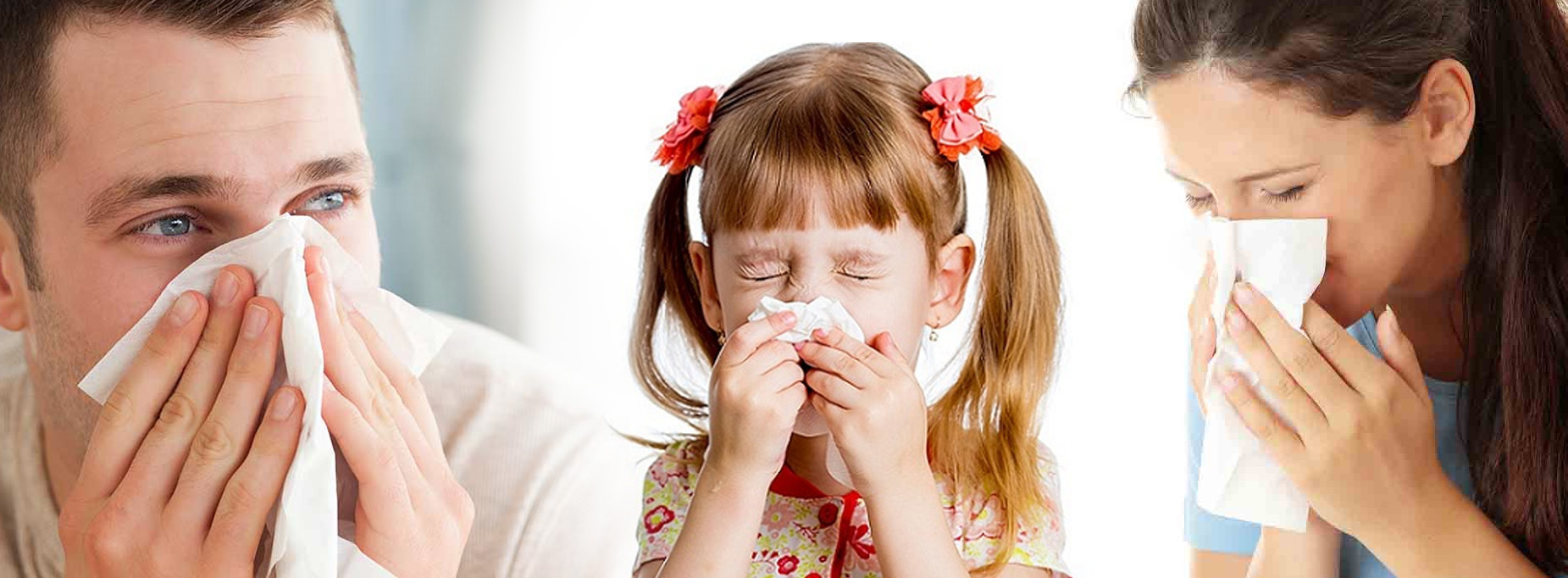

Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is a diagnosis associated with a group of symptoms affecting the nose. These symptoms occur when you breathe in something you are allergic to, such as dust, animal dander, or pollen. Symptoms can also occur when you eat a food that you are allergic to.
Allergic rhinitis is caused by an allergic reaction to an allergen, such as pollen, dust and certain animals.
Symptoms include runny nose; sneezing; itchy nose, mouth, throat, or eyes; and congestion. Other symptoms can also occur, such as tearing of the eyes, coughing, sore throat, wheezing, and headache.
People with mild allergic rhinitis have symptoms but they are not troublesome and do not interfere with daily activities such as school, work, or sleep. With moderate/severe allergic rhinitis, the symptoms are troublesome and affect daily life.
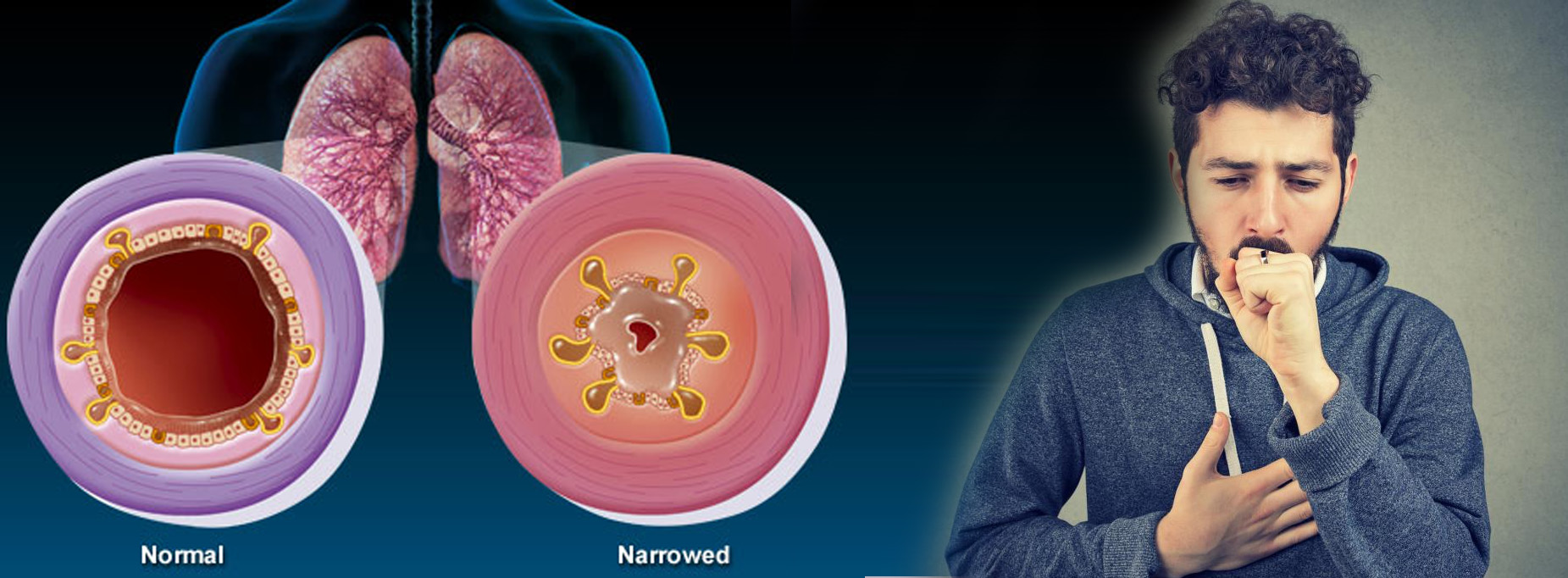
Allergic Bronchitis
Bronchitis can be acute, meaning it’s caused by a virus or bacteria, or it can be caused by allergies. Acute bronchitis usually goes away after a few days or weeks. Allergic bronchitis is chronic, and may be caused by exposure to allergy triggers like tobacco smoke, pollution, or dust. You may also hear it called chronic bronchitis.
Chronic bronchitis is part of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), along with emphysema. Chronic bronchitis can last for months or longer.
Bronchitis is inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes that carry air into your lungs. When you have bronchitis, your airways also produce too much mucus. Mucus normally protects your lungs by trapping bacteria, dust, and other particles before they can get in. Too much mucus makes it harder to breathe. People with bronchitis often cough a lot and have trouble breathing.
- A cough that produces mucus
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Tiredness
Cigarette smoking is the most common cause of chronic bronchitis. Smoke is filled with dangerous chemicals. When you breathe in cigarette smoke, it irritates the lining of your airways and makes your lungs produce extra mucus.
Other causes of chronic bronchitis include:- Air pollution
- Chemical fumes
- Dust
- Pollen
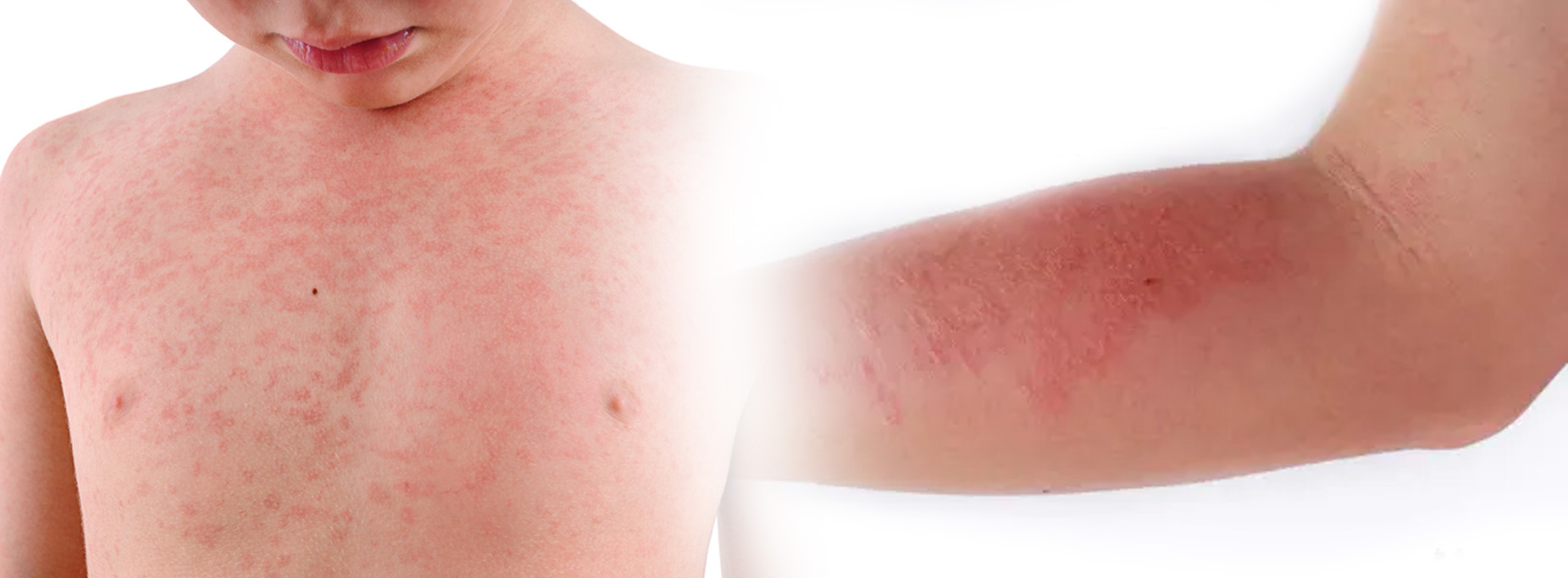
Urticaria
Hives are a red, raised, itchy skin rash that is sometimes triggered by an allergen. An allergen is something that produces an allergic reaction.
It is also known as urticaria, welts, weals, or nettle rash.
When an allergic reaction occurs, the body releases a protein called histamine. When histamine is released, the tiny blood vessels known as capillaries leak fluid. The fluid accumulates in the skin and causes a rash.
Urticaria occurs when the body reacts to an allergen and releases histamine and other chemicals from under the surface of the skin. The histamine and chemicals cause inflammation and fluid to accumulate under the skin, causing wheals.
- Anaphylaxis is a severe form of hypersensibility and is very often associated with urticaria and angioedema. Urticaria in an anaphylactic reaction is acute, developing rapidly following exposure to a potential trigger.
- Mastocytosis is a disease of mastocytes, the cells responsible for urticaria and angioedema.
- Systemic inflammatory diseases (auto-immune, such as lupus, vasculitis, and auto-inflammatory) are associated with other manifestations such as arthritis, photosensbility, Raynaud's syndrome and organ specific disease (kidneys, liver, lungs).
- Acute urticaria
- Chronic spontaneous urticaria
- Inducible urticaria
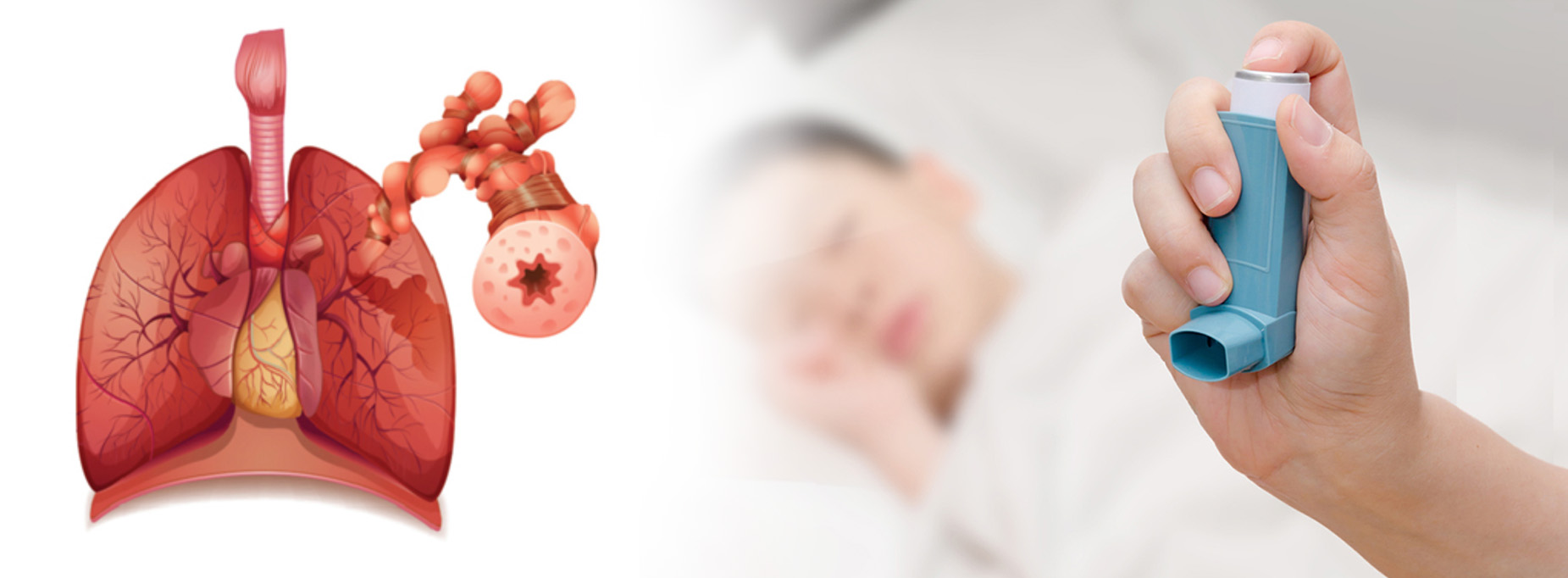
Bronchial Asthma
Asthma is a long term disease of the AIRWAYS which carry the air to the lungs. These airways becoe so narrow that it becomes difficult to breathe properly giving rise to acute attacks like breathlesness and wheezing. The air is unable to move in and out of the tubes freely.
- Allergic or Atopic asthma is also called EXTRINSIC asthma which may be precipitated due to Immunological reactions.
- Infective asthma is also known as INTRINSIC asthma caused by infection of the respiratory tract.
- Smoking
- Pollen grains
- Occupational : Asbestosis, Interstitial Lung Disease
- Allergy to dust, smoke,automobile exhausts or animal dander
- Infections of the bronchi, sinuses, tonsils or adenoids.
- Emotional factors
- Environmental changes in temperature and humidity
- exposure to noxious fumes.
- Strenous physical activity.
- Antihypertensive drugs like BETA BLOCKERS.
- Immune activation
- Coughing, especially at night, when laughing, or during exercise
- Wheezing, a squealing or whistling sound made when breathing
- Tightness in the chest
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
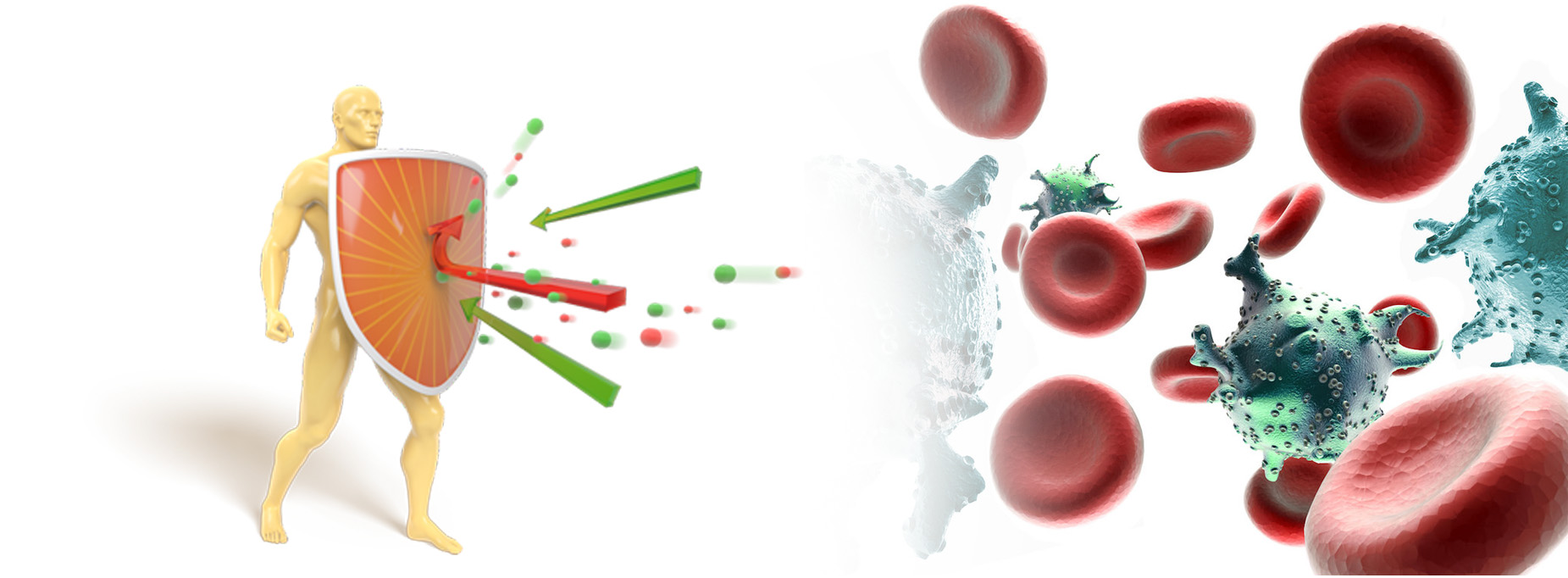
Immunodeficiency Disorders
Immunodeficiency disorders occur when the body's immune response is reduced or absent.
Immunodeficiency disorders prevent your body from fighting infections and diseases. This type of disorder makes it easier for you to catch viruses and bacterial infections.
Immunodeficiency disorders are either congenital or acquired. A congenital, or primary, disorder is one you were born with. Acquired, or secondary, disorders you get later in life. Acquired disorders are more common than congenital disorders.
- Immunodeficiency disorders disrupt your body’s ability to defend itself against bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
- There are two types of immunodeficiency disorders: those you are born with (primary), and those that are acquired (secondary).
- Anything that weakens your immune system can lead to a secondary immunodeficiency disorder.
- Spleen
- Tonsils
- Bone marrow
- Lymph nodes
These organs make and release lymphocytes. These are white blood cells classified as B cells and T cells. B and T cells fight invaders called antigens. B cells release antibodies specific to the disease your body detects. T cells destroy foreign or abnormal cells.
Examples of antigens that your B and T cells might need to fight off include:- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Cancer cells
- Parasites
An immunodeficiency disorder disrupts your body’s ability to defend itself against these antigens.
- Bone marrow
- Lymph nodes
- Parts of the spleen and gastrointestinal tract
- Thymus
- Tonsils